The source material for the production of water for pharmaceutical purposes should be water with drinking water parameters, according to locally applicable regulations. Usually, it is the Regulation of the Minister of Health on the quality of water intended for human consumption.
The state-of-art Purified Water (PW) generation process is based on membrane technologies such as reverse osmosis (RO), electrodeionization (EDI or CEDI) and membrane degassing. Membrane technologies allow for obtaining water with very good output parameters. However, they require a very carefully designed water pre-treatment system, in order to perform the following main tasks:
- Removal of suspended solids.
- Removal of iron and manganese compounds.
- Water softening or hardness stabilization.
- Removal or chemical binding of chlorine.
- Removal or chemical binding of carbon dioxide.
- Removal of colloidal impurities (to decrease value of the SDI15 index).
The most popular method of generation of Purified Water that meets the quality requirements set out in the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) is the technology of double-stage reverse osmosis.
For the generation of Purified Water with parameters compliant with the requirements of the US Pharmacopoeia, a combination of reverse osmosis and electrodeionization techniques is most often used. Depending on the level of salinity in the raw water, the electrodionisation can be preceded by single- or double-stage reverse osmosis.
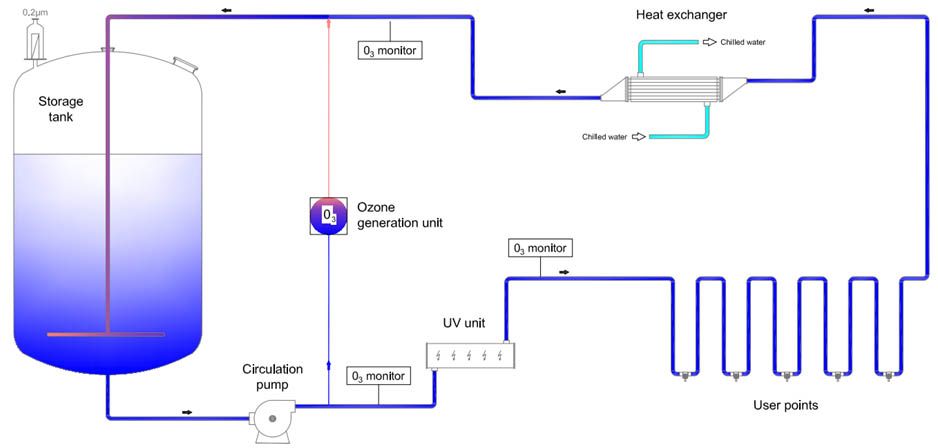
PW Storage and Distribution Systems.
The pharmaceutical water distribution system is usually organized in form of a circulation loop, assuring turbulent water motion in the pipes 24 hours a day and 7 days a week. In case of Purified Water, most often, the loop works in a cold mode, at temperature in the range of 15 – 25 °C. WFI water is usually stored hot, at temperature > 80 °C.
The main elements of the water distribution system are a storage tank and a circulation pump or pumps. The task of the storage tank is to compensate the peaks in water use. Circulation pumps are responsible for ensuring turbulent flow in pipelines and maintain the required pressure in the system. Depending on the number and location of consumption points, the distribution system may contain one or more circulation loops starting and ending in the storage tank.
Very often, UV units for water disinfection devices are installed at the PW loop feed lines to minimize the risk of bacterial growth in the system. UV disinfection devices that are installed in water distribution systems for the pharmaceutical industry must be free from dead-legs and completely drainable.
In PW cold water loops, it is necessary to install a heat exchanger, which protects against excessive temperature increase in the system due to energy from the pump transferred to the water as a result of frictions on the pipe walls in effect of constant circulation. Water distribution systems for the pharmaceutical industry use shell-and-tube heat exchangers of a special hygienic design, so-called DTS (Double Tube Sheet) type heat exchangers.
The PW storage and distribution system must undergo periodically sanitization. Automatic sanitation process is recommended. There are three main methods to sanitize purified water storage and distribution systems: